Product Description
Supply Ability 5000 Ton/Tons per Month
Packaging & delivery Packaging Details
Standard Seaworthy package or as the customer's requirement.
Port
ZheJiang Port or HangZhou Port
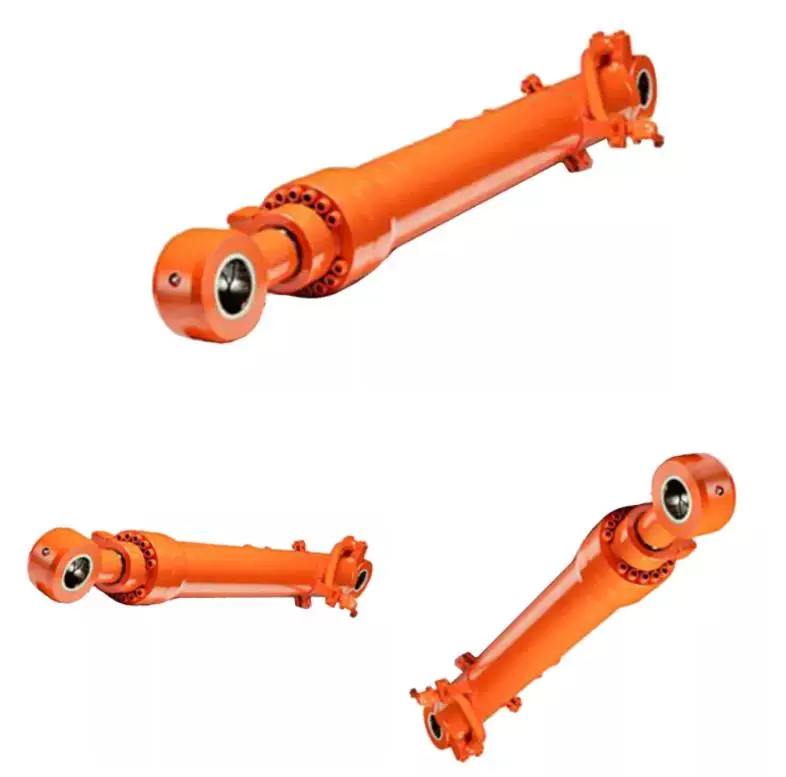
Picture Example:
Lead time:
| Quantity(tons) | 1 - 15 | 16 - 82 | >82 |
| Lead time (days) | 5 | 10 | To be negotiated |
Product Parameters
|
Product Name |
Seamless Steel Pipe |
|||
|
Standard |
ASTM A106-2006, ASTM A53-2007, API 5L, DIN 1626, DIN 17175, GB/T 8163-1999, JIS G3456-2004 |
|||
|
Grade |
10#, 20#, ST37, ST42, STB42, A53(A,B), A106(B,C) |
|||
|
Thickness |
1mm - 30mm |
|||
|
Section Shape |
Round |
|||
|
Place of Origin |
China |
|||
|
Application |
Structure Pipe |
|||
|
Technique |
Hot Rolled |
|||
|
Certification |
ISO |
|||
|
Alloy Or Not |
|
|||
|
Tolerance |
+5% |
|||
|
Type |
Seamless Steel Pipe |
|||
|
Processing Service |
Bending. Welding, Punching, Cutting |
|||
|
Keyword |
A106B A53B seamless steel pipe |
|||
|
MOQ |
1 Ton |
|||
|
DIN2391 ST52 H8 Cylinder Honed Pipe Honed Tube For Hydraulic Parts |
|||||
|
Inside Dia
(mm) |
ID Tolerance (mm) |
WT Tolerance
(mm) |
|||
|
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
||
|
≤30 |
+0.571/0 |
+0.033/0 |
+0.052/0 |
+0.084/0 |
±7.5% >210mm ±10% |
|
30 - ≤50 |
+0.571/0 |
+0.039/0 |
+0.062/0 |
+0.100/0 |
|
|
50 - ≤80 |
+0.030/0 |
+0.046/0 |
+0.074/0 |
+0.120/0 |
|
|
80 - ≤120 |
+0.035/0 |
+0.054/0 |
+0.087/0 |
+0.140/0 |
|
|
120 - ≤180 |
+0.040/0 |
+0.063/0 |
+0.100/0 |
+0.160/0 |
|
|
180 - ≤250 |
+0.046/0 |
+0.072/0 |
+0.115/0 |
+0.185/0 |
|
|
250 - ≤315 |
+0.052/0 |
+0.081/0 |
+0.130/0 |
+0.210/0 |
|
|
315 - ≤700 |
+0.057/0 |
+0.089/0 |
+0.140/0 |
+0.230/0 |
|
|
Steel Grade |
Chemical composition % |
|||||
|
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
Al |
|
|
≤ |
≥ |
|||||
|
20# |
0.17-0.24 |
0.17-0.37 |
0.35-0.65 |
0.035 |
0.035 |
/ |
|
45# |
0.42-0.50 |
0.17-0.37 |
0.50-0.80 |
0.035 |
0.035 |
/ |
|
Q345B |
≤0.2 |
≤0.5 |
1.00-1.60 |
0.03 |
0.03 |
/ |
|
Q345D |
≤0.2 |
≤0.5 |
1.00-1.60 |
0.03 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
|
25Mn |
0.22-0.29 |
0.17-0.37 |
0.70-1.00 |
0.035 |
0.035 |
/ |
|
27SiMn |
0.24-0.32 |
1.10-1.40 |
1.10-1.40 |
0.035 |
0.035 |
/ |
|
ST52 |
≤0.22 |
≤0.55 |
≤1.6 |
0.571 |
0.571 |
/ |
|
SAE1026 |
0.22-0.28 |
0.15-0.35 |
0.60-0.90 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
/ |
|
Delivery Condition |
cold finished (hard) (BK) |
cold drawn and stress-relieved (BK+S) |
|||
|
Steel Grade |
Tensile Strength (Mpa) |
Elongation (%) |
Tensile Strength (Mpa) |
Yield Strength (Mpa) |
Elongation (%) |
|
20# |
≥550 |
≥8 |
≥520 |
≥375 |
≥15 |
|
45# |
≥640 |
≥5 |
≥600 |
≥520 |
≥10 |
|
16Mn |
≥640 |
≥5 |
≥600 |
≥520 |
≥14 |
|
25Mn |
≥640 |
≥5 |
≥600 |
≥510 |
≥15 |
|
27SiMn |
≥800 |
≥5 |
≥760 |
≥610 |
≥10 |
|
ST52 |
≥640 |
≥5 |
≥600 |
≥520 |
≥14 |
|
SAE1026 |
≥640 |
≥5 |
≥600 |
≥510 |
≥15 |
| Certification: | GS, RoHS, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | High Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | High Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Single Acting |
| Structure: | Piston Type |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do hydraulic cylinders ensure smooth and consistent movement in heavy machinery?
Hydraulic cylinders play a vital role in ensuring smooth and consistent movement in heavy machinery. Their design and operation allow for precise control over the motion of heavy loads, resulting in efficient and reliable performance. Here's a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders contribute to smooth and consistent movement in heavy machinery:
1. Hydraulic Fluid and Pressure:
- Hydraulic cylinders operate by utilizing hydraulic fluid, typically oil, to transmit force and motion. The fluid is pressurized by a hydraulic pump, creating a force that acts on the piston inside the cylinder. The pressure of the hydraulic fluid can be precisely controlled, allowing for smooth and gradual movement of heavy machinery. The fluid's incompressibility ensures that the force is evenly distributed, resulting in consistent and predictable motion.
2. Piston and Cylinder Design:
- Hydraulic cylinders are designed with precision to ensure smooth movement. The piston and cylinder bore are machined to tight tolerances, reducing friction and minimizing internal leakage. This precise fit between the piston and cylinder walls helps maintain consistent motion without jerks or sudden changes in speed. Additionally, the use of high-quality seals and lubrication further enhances the smooth operation of the cylinder.
3. Control Valves and Flow Control:
- Hydraulic systems incorporate control valves that regulate the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the cylinder. These valves allow for precise control over the speed and direction of the cylinder's movement. By adjusting the flow rate, operators can achieve smooth and controlled motion of heavy machinery, avoiding sudden starts or stops. Flow control valves also enable speed adjustment, ensuring consistent movement even under varying loads or operating conditions.
4. Cushioning and Damping:
- Hydraulic cylinders can be equipped with cushioning mechanisms to absorb shock and minimize impacts during the movement of heavy machinery. Cushioning is achieved by incorporating specialized valves or adjustable orifices in the cylinder, which restrict the flow of hydraulic fluid near the end of the stroke. This gradual deceleration helps prevent sudden jolts or vibrations, maintaining smooth and consistent movement while reducing stress on the machinery and its components.
5. Load Balancing:
- Hydraulic cylinders can be designed and arranged in a system to balance the load and distribute forces evenly. By utilizing multiple cylinders in parallel or series configurations, heavy machinery can achieve balanced movement, preventing uneven stress and ensuring smooth operation. Load balancing also helps minimize the risk of component failure and enhances the overall stability and longevity of the machinery.
6. Feedback and Control Systems:
- Advanced hydraulic systems incorporate feedback sensors and control systems to monitor and adjust the movement of heavy machinery. These sensors provide real-time information about the position, speed, and force exerted by the hydraulic cylinders. The control system processes this data and adjusts the flow of hydraulic fluid accordingly to maintain smooth and consistent movement. By continuously monitoring and regulating the cylinder's operation, feedback and control systems contribute to precise and reliable motion control.
7. Maintenance and Servicing:
- Regular maintenance and servicing of hydraulic cylinders are essential to ensure their smooth and consistent movement in heavy machinery. Proper lubrication, inspection of seals, and replacement of worn-out components help maintain optimal performance. Preventive maintenance practices, such as filter replacements and fluid analysis, also contribute to the longevity and reliability of hydraulic systems, ensuring consistent movement over time.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders ensure smooth and consistent movement in heavy machinery through the use of hydraulic fluid and pressure, precise piston and cylinder design, control valves and flow control, cushioning and damping mechanisms, load balancing, feedback and control systems, and regular maintenance and servicing. By leveraging these features, hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary force and control to handle heavy loads while maintaining precise and reliable motion, enhancing the overall performance and productivity of heavy machinery in various industrial applications.

Handling the Challenges of Minimizing Fluid Leaks and Contamination in Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders face challenges when it comes to minimizing fluid leaks and contamination, as these issues can impact the performance, reliability, and lifespan of the system. However, there are several measures and design considerations that help address these challenges effectively. Let's explore how hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination:
- Sealing Systems: Hydraulic cylinders employ advanced sealing systems to prevent fluid leaks. These systems typically include various types of seals, such as piston seals, rod seals, and wiper seals. The seals are designed to create a tight and reliable barrier between the moving components of the cylinder and the external environment, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage.
- Seal Material Selection: The choice of seal materials is crucial in minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. Hydraulic cylinder manufacturers carefully select seal materials that are compatible with the hydraulic fluid used and resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemical degradation. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the seals, reducing the likelihood of leaks or premature seal failure.
- Proper Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance of hydraulic cylinders is essential for minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. During installation, attention should be given to proper alignment, torqueing of bolts, and adherence to recommended procedures. Regular maintenance includes inspecting seals, replacing worn-out components, and addressing any signs of leakage promptly. Proper maintenance practices help identify and rectify issues before they escalate and cause significant problems.
- Contamination Control: Hydraulic cylinders incorporate measures to control contamination and maintain fluid cleanliness. This includes the use of filtration systems, such as in-line filters, to remove particles and contaminants from the hydraulic fluid. Additionally, hydraulic reservoirs often have breathers and desiccant filters to prevent moisture and airborne contaminants from entering the system. By controlling contamination, hydraulic cylinders minimize the risk of damage to internal components and maintain optimal system performance.
- Environmental Protection: Hydraulic cylinders may be equipped with protective features to safeguard against external contaminants. For example, bellows or protective boots can be installed to shield the rod and seals from debris, dirt, or moisture present in the operating environment. These protective measures help extend the life of the seals and enhance the overall reliability of the hydraulic cylinder.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders employ sealing systems, appropriate seal materials, proper installation and maintenance practices, contamination control measures, and environmental protection features to handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. By implementing these measures, manufacturers can ensure reliable and long-lasting hydraulic cylinder performance, minimize the risk of fluid leakage, and maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic system.

How do hydraulic cylinders handle variations in load and pressure during operation?
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to handle variations in load and pressure during operation, making them versatile and efficient in various applications. Hydraulic systems use the principle of transmitting force through incompressible fluid to generate linear motion. Here's a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders handle variations in load and pressure:
1. Load Handling:
- Hydraulic cylinders are capable of handling different loads by utilizing the principle of Pascal's law. According to Pascal's law, when pressure is applied to a fluid in a confined space, the pressure is transmitted equally in all directions. In a hydraulic cylinder, the force applied to the piston results in an equal force output at the rod end of the cylinder. The size of the piston and the pressure exerted determine the force generated by the cylinder. Therefore, hydraulic cylinders can handle a wide range of loads by adjusting the pressure applied to the fluid.
2. Pressure Compensation:
- Hydraulic systems incorporate pressure compensation mechanisms to handle variations in pressure during operation. Pressure compensating valves or regulators are often used to maintain a consistent pressure in the hydraulic system, regardless of load changes. These valves automatically adjust the flow rate or pressure to ensure stable and controlled operation of the hydraulic cylinder. By compensating for pressure variations, hydraulic cylinders can maintain a consistent force output and prevent damage or instability due to excessive pressure.
3. Control Valves:
- Control valves play a crucial role in managing variations in pressure and load during hydraulic cylinder operation. Directional control valves, such as spool valves or poppet valves, control the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the cylinder, enabling precise control of the cylinder's extension and retraction. By adjusting the position of the control valve, the speed and force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder can be regulated to match the load and pressure requirements of the application. Control valves allow for efficient handling of variations in load and pressure by providing fine-tuned control over the hydraulic system.
4. Accumulators:
- Hydraulic accumulators are often used to handle fluctuations in pressure and load. Accumulators store hydraulic fluid under pressure, which can be released or absorbed as needed to compensate for sudden changes in load or pressure. When the load on the hydraulic cylinder decreases, the accumulator releases stored fluid to maintain pressure and prevent pressure spikes. Conversely, when the load on the cylinder increases, the accumulator absorbs excess fluid to maintain system stability. By utilizing accumulators, hydraulic cylinders can effectively handle variations in load and pressure, ensuring smooth and controlled operation.
5. Feedback and Control Systems:
- Advanced hydraulic systems may incorporate feedback and control systems to monitor and adjust the operation of hydraulic cylinders in real-time. Position sensors or pressure sensors provide feedback on the cylinder's position, force, and pressure, allowing the control system to make continuous adjustments to optimize performance. These systems can automatically adapt to variations in load and pressure, ensuring precise control and efficient operation of the hydraulic cylinder.
6. Design Considerations:
- Proper design considerations, such as selecting the appropriate cylinder size, piston diameter, and rod diameter, are essential for handling variations in load and pressure. The design should account for the maximum anticipated load and pressure conditions to ensure the hydraulic cylinder operates within its specified range. Additionally, the selection of suitable seals, materials, and components that can withstand the anticipated load and pressure variations is crucial for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the hydraulic cylinder.
By utilizing the principles of hydraulic systems, incorporating pressure compensation mechanisms, employing control valves and accumulators, and implementing feedback and control systems, hydraulic cylinders can effectively handle variations in load and pressure during operation. These features and design considerations allow hydraulic cylinders to adapt and perform optimally in a wide range of applications and operating conditions.

editor by CX 2023-11-25