Product Description
Model Number: ISO219-40-150
valve:QF-2C
Material: Steel 37Mn
new seamless steel gas cylinder for N2,O2
Industrial nitrogen Gas
Pressure: High
Place of Origin: China (Mainland)
Brand Name: DSW
Thickness of seamless:5.7mm
weight of seamless: 47to 50kg
working pressure:150bar
test pressure: 250bar
TP:250KG/CM2
PW:150KG/CM2
| 40L and 50L medical oxygen cylinders |
|||||||
| Type | (mm) Outside Diameter |
(L) Water Capacity |
(mm)
Height |
(Kg) Weight(Without valve,cap) |
(Mpa) Working Pressure |
(mm) Design Wall Thickness |
Material Grades |
| ISO232-40-150 | 219 | 40 | 1167 | 43 | 200 | 5.2 | 37Mn |
| ISO232-47-150 | 47 | 1351 | 49 | ||||
| ISO232-50-150 | 50 | 1430 | 51.6 | ||||
| ISO232-40-200 | 232 | 40 | 1156 | 44.9 | 200 | 5.2 | 34CrMo4 |
| ISO232-46.7-200 | 46.7 | 1333 | 51 | ||||
| ISO232-47-200 | 47 | 1341 | 51.3 | ||||
| ISO232-50-200 | 50 | 1420 | 54 | ||||
| EN232-40-210 | 232(TPED) | 40 | 1156 | 44.9 | 230 | 5.8 | 34CrMo4 |
| EN232-46.7-210 | 46.7 | 1333 | 51 | ||||
| EN232-47-210 | 47 | 1341 | 51.3 | ||||
| EN232-50-210 | 50 | 1420 | 54 | ||||
| EN232-40-230 | 40 | 1156 | 44.9 | 230 | 5.8 | 34CrMo4 | |
| EN232-46.7-230 | 46.7 | 1333 | 51 | ||||
| ISO232-47-230 | 47 | 1341 | 51.3 | ||||
| ISO232-50-230 | 50 | 1420 | 54 | ||||
| ISO267-40-150 | 267 | 40 | 922 | 43.3 | 150 | 5.8 | 37Mn |
| ISO267-50-150 | 50 | 1119 | 51.3 | ||||
100% new high quality seamless steel pipe from Bao Shan Iron co.,ltd (Baosteel).
Total 5 working line make 3000pcs per day for oxygen gas cylinder, argon gas cylinder, helium gas cylinder, Nitrogen gas cylinder , Co2 gas cylinder, N2O gas cylinder..etc
China top 1 advanced heat treatment machine. And China top 1 internal polishing machine to make high purity gas cylinder with 99.999% oxygen gas, helium gas, N2O gas and argon gas.
100% Hydrostatic prssure test and leakage test to keep the quality
Advanced automatic spraying working line make the spraying at high top quality , no any bubble , without shrinkage and distoration .
Japan imported shoulder marking machine make it the most qualified ones .
DSW seamless gas cylinder have nice appearance shoulders because we use shape-correction machine treatment make the cylinder shoulder most beautiful shape which other supplier can't be compared.
Laboratory test standard ISO9809-3 and ISO9809-1, DOT-3AA, EN1964,GB5099 ..etc
Specification
| RECORD OF HYDROSTATIC TESTS ON CYLINDERS TIME ≥ 60S |
||||||||
| S.N | Serial No. | The weight without valve&cap(kg) | Volumetric Capacity(L) | Total expansion(ml) | Permanent expansion(ml) | Percent of Permanent to totalexpanison(%) | Test Pressure 250Bar | Lot and Batch No. |
| 401 | 2070968 057 | 48.6 | 40.0 | 200.3 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 402 | 2070968 058 | 48.3 | 40.0 | 204.2 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 403 | 2070968 059 | 48.2 | 40.1 | 205.1 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 404 | 2070968 060 | 48.5 | 40.1 | 195.2 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 405 | 2070968 061 | 48.2 | 40.1 | 205.1 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 406 | 2070968 062 | 48.6 | 40.0 | 206.2 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 407 | 2070968 063 | 48.3 | 40.3 | 193.9 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 408 | 2070968 064 | 48.0 | 40.1 | 200.1 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 409 | 2070968 065 | 48.4 | 40.0 | 205.2 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 410 | 2070968 066 | 47.9 | 40.1 | 200.1 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 411 | 2070968 067 | 47.9 | 40.2 | 201.0 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 412 | 2070968 068 | 48.7 | 40.0 | 200.3 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 413 | 2070968 069 | 48.3 | 40.2 | 201.0 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 414 | 2070968 070 | 48.2 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 415 | 2070968 071 | 47.9 | 40.0 | 206.2 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 416 | 2070968 072 | 48.5 | 40.4 | 193.8 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 417 | 2070968 073 | 49.0 | 40.0 | 201.3 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 418 | 2070968 074 | 49.2 | 40.1 | 201.1 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 419 | 2070968 075 | 48.3 | 40.2 | 196.0 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 420 | 2070968 076 | 47.7 | 40.2 | 198.0 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 421 | 2070968 077 | 48.2 | 40.2 | 198.0 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 422 | 2070968 078 | 48.5 | 40.3 | 201.8 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 423 | 2070968 079 | 49.2 | 40.1 | 194.2 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 424 | 2070968 080 | 48.5 | 40.4 | 200.7 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 425 | 2070968 081 | 48.2 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 426 | 2070968 082 | 48.3 | 40.0 | 200.3 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 427 | 2070968 083 | 48.5 | 40.3 | 197.9 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 428 | 2070968 084 | 48.3 | 40.1 | 200.1 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 429 | 2070968 085 | 48.6 | 40.1 | 194.2 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 430 | 2070968 086 | 48.5 | 40.1 | 199.1 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 431 | 2070968 087 | 48.4 | 40.1 | 199.1 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 432 | 2070968 088 | 48.1 | 40.2 | 203.9 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 433 | 2070968 089 | 48.6 | 40.2 | 198.0 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 434 | 2070968 090 | 48.0 | 40.2 | 201.0 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 435 | 2070968 091 | 49.6 | 40.0 | 206.2 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 436 | 2070968 092 | 48.5 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 437 | 2070968 093 | 48.1 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 438 | 2070968 094 | 48.0 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 439 | 2070968 095 | 48.1 | 40.1 | 197.2 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 440 | 2070968 096 | 48.3 | 40.1 | 199.1 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 441 | 2070968 097 | 48.1 | 40.2 | 203.0 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 442 | 2070968 098 | 48.6 | 40.1 | 199.1 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 443 | 2070968 099 | 48.5 | 40.2 | 198.0 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 444 | 2070968 100 | 48.4 | 40.1 | 202.1 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 445 | 2070968 101 | 48.7 | 40.0 | 204.2 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 446 | 2070968 102 | 49.2 | 40.0 | 204.2 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 447 | 2070968 103 | 48.1 | 40.2 | 200.0 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 448 | 2070968 104 | 48.0 | 40.1 | 202.1 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 449 | 2070968 105 | 48.3 | 40.1 | 196.2 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 250 | 2070968 |
| 450 | 2070968 106 | 48.8 | 40.0 | 206.2 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 250 | 2070968 |
| Material: | Steel |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Oxygen Gas and Nitrogen Cylinder |
| Structure: | Gas - Liquid Damping Cylinder |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Pressure Direction: | Single-acting Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
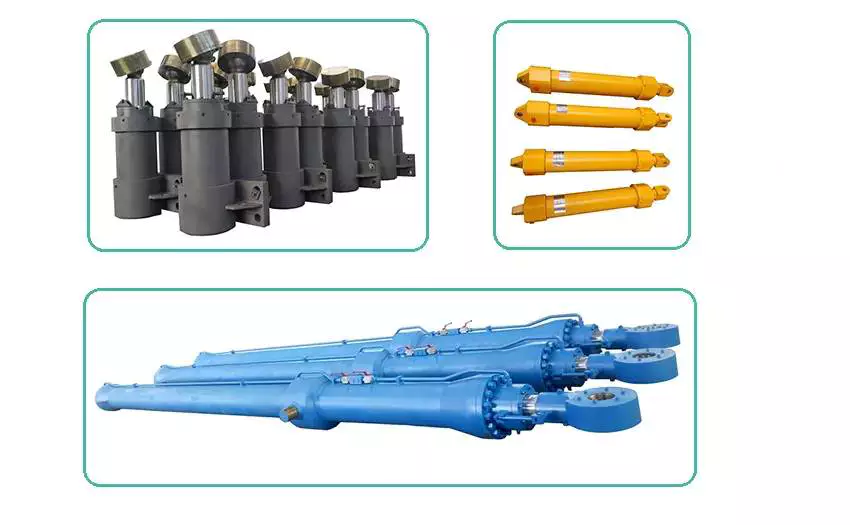

How do hydraulic cylinders compare to other methods of force generation like electric motors?
Hydraulic cylinders and electric motors are two different methods of force generation with distinct characteristics and applications. While both hydraulic cylinders and electric motors can generate force, they differ in terms of their working principles, performance attributes, and suitability for specific applications. Here's a detailed comparison of hydraulic cylinders and electric motors:
1. Working Principle:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders generate force through the conversion of fluid pressure into linear motion. They consist of a cylinder barrel, piston, piston rod, and hydraulic fluid. When pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, causing the piston rod to extend or retract, thereby generating linear force.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors generate force through the conversion of electrical energy into rotational motion. They consist of a stator, rotor, and electromagnetic field. When an electrical current is applied to the motor's windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor, causing it to rotate and generate torque.
2. Force and Power:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are known for their high force capabilities. They can generate substantial linear forces, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that require lifting, pushing, or pulling large loads. Hydraulic systems can provide high force output even at low speeds, allowing for precise control over force application. However, hydraulic systems typically operate at lower speeds compared to electric motors.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors excel in providing high rotational speeds and are commonly used for applications that require rapid motion. While electric motors can generate significant torque, they tend to have lower force output compared to hydraulic cylinders. Electric motors are suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.
3. Control and Precision:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems offer excellent control over force, speed, and positioning. By regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and speed of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely controlled. Hydraulic systems can provide gradual acceleration and deceleration, allowing for smooth and precise movements. This level of control makes hydraulic cylinders well-suited for applications that require precise positioning, such as in industrial automation or construction equipment.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors also offer precise control over speed and positioning. Through motor control techniques such as varying voltage, frequency, or pulse width modulation (PWM), the rotational speed and position of electric motors can be accurately controlled. Electric motors are commonly used in applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics, CNC machines, or servo systems.
4. Efficiency and Energy Consumption:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems can be highly efficient, especially when properly sized and designed. However, hydraulic systems typically have higher energy losses due to factors such as fluid leakage, friction, and heat generation. The overall efficiency of a hydraulic system depends on the design, component selection, and maintenance practices. Hydraulic systems require a hydraulic power unit to pressurize the hydraulic fluid, which consumes additional energy.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors can have high efficiency, especially when operated at their optimal operating conditions. Electric motors have lower energy losses compared to hydraulic systems, primarily due to the absence of fluid leakage and lower friction losses. The overall efficiency of an electric motor depends on factors such as motor design, load conditions, and control techniques. Electric motors require an electrical power source, and their energy consumption depends on the motor's power rating and the duration of operation.
5. Environmental Considerations:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems typically use hydraulic fluids that can pose environmental concerns if they leak or are not properly disposed of. The choice of hydraulic fluid can impact factors such as biodegradability, toxicity, and potential environmental hazards. Proper maintenance and leak prevention practices are essential to minimize the environmental impact of hydraulic systems.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors are generally considered more environmentally friendly since they do not require hydraulic fluids. However, the environmental impact of electric motors depends on the source of electricity used to power them. When powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, electric motors can offer a greener solution compared to hydraulic systems.
6. Application Suitability:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used in applications that require high force output, precise control, and durability. They are widely employed in industries such as construction, manufacturing, mining, and aerospace. Hydraulic systems are well-suited for heavy-duty applications, such as lifting heavy objects, operating heavy machinery, or controlling large-scale movements.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors are widely used in various industries and applications that require rotational motion, speed control, and precise positioning. They are commonly found in appliances, transportation, robotics, HVAC systems, and automation. Electric motorsare suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.In summary, hydraulic cylinders and electric motors have different working principles, force capabilities, control characteristics, efficiency levels, and application suitability. Hydraulic cylinders excel in providing high force output, precise control, and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Electric motors, on the other hand, offer high rotational speeds, precise speed control, and are commonly used for applications that involve continuous rotary motion. The choice between hydraulic cylinders and electric motors depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of motion, force output, control precision, and environmental considerations.
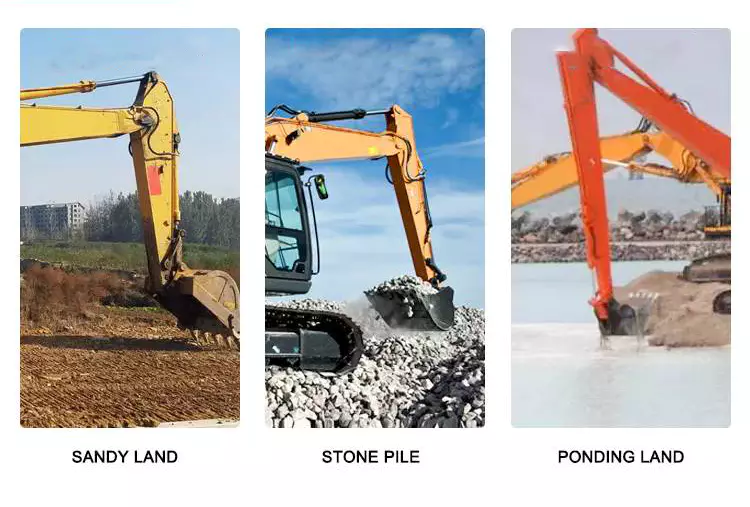

Can you provide real-world examples of machinery that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders?
Hydraulic cylinders are widely used in various industries and applications due to their ability to provide powerful and precise linear motion. They play a crucial role in enabling the operation of heavy machinery that requires controlled force and movement. Here are some real-world examples of machinery that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders:
1. Construction Equipment:
- Hydraulic cylinders are extensively used in construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and cranes. These machines rely on hydraulic cylinders to perform tasks like lifting heavy loads, extending and retracting booms, tilting buckets, and controlling the movement of various components. Hydraulic cylinders provide the power and precision required to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads encountered in construction projects.
2. Agricultural Machinery:
- Many agricultural machines, including tractors, combine harvesters, and sprayers, utilize hydraulic cylinders for critical operations. Hydraulic cylinders are used to control the movement of attachments, such as front loaders, backhoes, and plows. They enable functions like lifting and lowering implements, adjusting cutting heights, and controlling the positioning of harvesting equipment. Hydraulic cylinders enhance efficiency and productivity in agricultural operations.
3. Material Handling Equipment:
- Hydraulic cylinders are integral components of material handling equipment, such as forklifts, pallet jacks, and cranes. These machines rely on hydraulic cylinders to lift and lower loads, tilt platforms or forks, and control the movement of lifting mechanisms. Hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary strength and precision to handle heavy loads and ensure safe and efficient material handling operations.
4. Industrial Machinery:
- Various industrial machinery and equipment heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders for critical functions. Examples include hydraulic presses, injection molding machines, metal-forming machines, and hydraulic-powered robots. Hydraulic cylinders enable precise control of force and movement in these applications, allowing for accurate shaping, pressing, and assembly processes.
5. Mining Equipment:
- Hydraulic cylinders are extensively used in mining machinery and equipment. Underground mining machines, such as continuous miners and longwall shearers, utilize hydraulic cylinders for cutting, shearing, and roof support operations. Surface mining equipment, including hydraulic shovels, draglines, and haul trucks, rely on hydraulic cylinders for tasks like bucket movement, boom extension, and vehicle suspension.
6. Automotive Industry:
- The automotive industry extensively utilizes hydraulic cylinders in various applications. Hydraulic cylinders are employed in vehicle suspension systems, power steering systems, convertible tops, and hydraulic brake systems. They enable smooth and controlled movement, precise steering, and efficient braking in automobiles.
7. Aerospace and Aviation:
- Hydraulic cylinders are utilized in aerospace and aviation applications, such as aircraft landing gear systems, wing flaps, and cargo handling equipment. Hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary force and control for extending and retracting landing gear, adjusting wing flaps, and operating cargo doors, ensuring safe and reliable aircraft operations.
8. Marine and Offshore Industry:
- Hydraulic cylinders are essential components in marine and offshore equipment, including ship cranes, winches, and hydraulic-powered anchor systems. They enable lifting, lowering, and positioning of heavy loads, as well as the control of various marine equipment.
These are just a few examples of machinery and industries that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders. The versatility, power, and precise control offered by hydraulic cylinders make them indispensable in a wide range of applications, where controlled linear motion and force are essential.

Can you explain the role and significance of hydraulic cylinders in machinery?
Hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in machinery across various industries. They are essential components that provide controlled and powerful linear motion, enabling the operation of heavy equipment and facilitating numerous tasks. The role and significance of hydraulic cylinders in machinery can be explained in detail as follows:
Role of Hydraulic Cylinders:
- Conversion of Hydraulic Energy: Hydraulic cylinders convert hydraulic energy, typically in the form of pressurized hydraulic fluid, into linear force and motion. This conversion allows machinery to perform tasks such as lifting, pushing, pulling, clamping, tilting, and controlling various mechanisms.
- Generation of Linear Motion: Hydraulic cylinders generate linear motion by utilizing the principles of Pascal's law. When hydraulic fluid is directed into one side of the cylinder, it applies pressure on the piston, resulting in linear movement of the piston and the attached piston rod. This linear motion can be used to actuate other components within the machinery or directly perform the required task.
- Force Generation: Hydraulic cylinders are capable of generating high forces due to the hydraulic pressure applied to the piston. The force output of a hydraulic cylinder depends on the surface area of the piston and the pressure of the hydraulic fluid. This force allows machinery to exert significant power for lifting heavy loads, applying pressure, or overcoming resistance.
- Precise Control: Hydraulic cylinders offer precise control over the linear motion and force exerted. By regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, the speed and direction of the cylinder's movement can be accurately adjusted. This level of control is crucial in machinery that requires precise positioning, delicate movements, or synchronization of multiple cylinders.
- Integration with Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic cylinders are integral parts of hydraulic systems used in machinery. They work in conjunction with hydraulic pumps, valves, and actuators to create a complete hydraulic circuit. This integration allows for efficient power transmission, control, and coordination of various machine functions.
Significance of Hydraulic Cylinders:
- Heavy Equipment Operation: Hydraulic cylinders are vital in heavy machinery used in construction, mining, agriculture, material handling, and other industries. They enable the lifting and movement of heavy loads, the operation of attachments, and the performance of tasks that require high force and precision.
- Versatility and Adaptability: Hydraulic cylinders are versatile components that can be designed and tailored to meet specific machinery requirements. They can be integrated into various types of equipment and customized based on factors such as force capacity, stroke length, speed, and mounting options. This adaptability makes hydraulic cylinders suitable for diverse applications.
- Durability and Reliability: Hydraulic cylinders are built to withstand rigorous operating conditions, including high pressures, heavy loads, and continuous use. They are designed with robust materials, precise machining, and effective sealing systems to ensure durability and reliability over extended periods of operation.
- Safety and Load Control: Hydraulic cylinders provide safe and controlled operation in machinery. They offer overload protection mechanisms, such as relief valves, to prevent damage caused by excessive force or pressure. Additionally, hydraulic cylinders allow for precise load control, minimizing the risk of accidents during lifting, lowering, or positioning of heavy loads.
- Compact Design: Hydraulic cylinders offer a high power-to-size ratio, allowing for compact machinery design. Their relatively small size compared to the forces they can generate makes them suitable for applications where space is limited or weight restrictions apply.
- Energy Efficiency: Hydraulic cylinders contribute to energy efficiency in machinery. The use of hydraulic systems allows for the transfer of power over long distances without significant power losses. Additionally, hydraulic cylinders can incorporate energy-saving features such as load-sensing technology and regenerative circuits, reducing energy consumption.
Overall, hydraulic cylinders play a vital role in machinery by providing controlled and powerful linear motion. Their significance lies in their ability to convert hydraulic energy, generate high forces, offer precise control, integrate with hydraulic systems, and facilitate the operation of heavy equipment across various industries. Hydraulic cylinders contribute to increased productivity, safety, and efficiency in machinery applications, making them indispensable components in modern-day engineering.

editor by CX 2023-11-21