Product Description
Company introduction
HangZhou CHINAMFG INDUSTRY CO.,LTD established in 1998. we produce the following gas: 99.999% and 99.995% helium were 99.9% and 99.999%, 99.9% and 99.999% of the laughing gas, the carbon monoxide were 99.9993% and 99.999%, 99.9993% and 99.999% of argon gas, and 99.995% hydrogen, 99.995% and 99.999% nitrogen, 99.999% and 99.99% were 99.999% and 99.995% and 99.999% of carbon dioxide, methane, 99.999% and 99.998%, and 99.999% of the oxygen, or more than 99.9% of acetylene, and so on.
So far our products are enjoying good markets at home and exporting to Asia, Middle East ,South America and European
Product introduction
1,99.999% oxygen gas filled in 40L cylinder ,filling pressure:150bar, static pressure:135+_5bar
With QF-2C valve with cap JP brand BTIC cylinder:
2,99.999% helium gas filled in 40L cylinder ,filling pressure:150bar, static pressure:135+_5bar
With QF-2D valve with cap JP brand BTIC cylinder.
3, 99.9% N2O gas filled in 40L cylinder gas vol 20kg/cylinder With QF-2C valve with cap JP brand BTIC cylinder
4, 99.9% N2O gas filled in 40L Cylinder , Gas vol.20kg/cylinder
Valve: QF-2
Volume: ~40L
Diameter: 219 Mm
Working Pressure: 150 Bar
Testing Pressure: 250 Bar
Color: Skyblue
5, 99.9% N2O gas filled in 10L Cylinder , Gas vol.5kg/cylinder
Valve: QF-2
Volume: ~40L
Diameter: 219 Mm
Working Pressure: 150 Bar
Testing Pressure: 250 Bar
Color: Skyblue
| Type | (mm) Outside Diameter |
(L) Water Capacity |
(mm) () Height (Withoutvalve) |
(Kg) (,) Weight(Without valve,cap) |
(Mpa) Working Pressure |
(mm) Design Wall Thickness |
Material Grades |
| ISO102-1.8-150 | 102 | 1.8 | 325 | 3.5 | 150 | 3 | 37Mn |
| ISO102-3-150 | 3 | 498 | 5.2 | ||||
| ISO102-3.4-150 | 3.4 | 555 | 5.7 | ||||
| ISO102-4.4-150 | 4.4 | 700 | 7.2 | ||||
| ISO108-1.4-150 | 108 | 1.4 | 240 | 2.9 | 150 | 3.2 | 37Mn |
| ISO108-1.8-150 | 1.8 | 285 | 3.3 | ||||
| ISO108-2-150 | 2 | 310 | 3.6 | ||||
| ISO108-3-150 | 3 | 437 | 4.9 | ||||
| ISO108-3.6-150 | 3.6 | 515 | 5.7 | ||||
| ISO108-4-150 | 4 | 565 | 6.2 | ||||
| ISO108-5-150 | 5 | 692 | 7.5 | ||||
| ISO140-3.4-150 | 140 | 3.4 | 321 | 5.8 | 150 | 4.1 | 37Mn |
| ISO140-4-150 | 4 | 365 | 6.4 | ||||
| ISO140-5-150 | 5 | 440 | 7.6 | ||||
| ISO140-6-150 | 6 | 515 | 8.8 | ||||
| ISO140-6.3-150 | 6.3 | 545 | 9.2 | ||||
| ISO140-6.7-150 | 6.7 | 567 | 9.5 | ||||
| ISO140-7-150 | 7 | 595 | 9.9 | ||||
| ISO140-7.5-150 | 7.5 | 632 | 10.5 | ||||
| ISO140-8-150 | 8 | 665 | 11 | ||||
| ISO140-9-150 | 9 | 745 | 12.2 | ||||
| ISO140-10-150 | 10 | 830 | 13.5 | ||||
| ISO140-11-150 | 11 | 885 | 14.3 | ||||
| ISO140-13.4-150 | 13.4 | 1070 | 17.1 | ||||
| ISO140-14-150 | 14 | 1115 | 17.7 | ||||
| ISO159-7-150 | 159 | 7 | 495 | 9.8 | 150 | 4.7 | 37Mn |
| ISO159-8-150 | 8 | 554 | 10.8 | ||||
| ISO159-9-150 | 9 | 610 | 11.7 | ||||
| ISO159-10-150 | 10 | 665 | 12.7 | ||||
| ISO159-11-150 | 11 | 722 | 13.7 | ||||
| ISO159-12-150 | 12 | 790 | 14.8 | ||||
| ISO159-12.5-150 | 12.5 | 802 | 15 | ||||
| ISO159-13-150 | 13 | 833 | 15.6 | ||||
| ISO159-13.4-150 | 13.4 | 855 | 16 | ||||
| ISO159-13.7-150 | 13.7 | 878 | 16.3 | ||||
| ISO159-14-150 | 14 | 890 | 16.5 | ||||
| ISO159-15-150 | 15 | 945 | 17.5 | ||||
| ISO159-16-150 | 16 | 1000 | 18.4 | ||||
| ISO180-8-150 | 180 | 8 | 480 | 13.8 | 150 | 5.3 | 37Mn |
| ISO180-10-150 | 10 | 570 | 16.1 | ||||
| ISO180-12-150 | 12 | 660 | 18.3 | ||||
| ISO180-15-150 | 15 | 790 | 21.6 | ||||
| ISO180-20-150 | 20 | 1015 | 27.2 | ||||
| ISO180-21-150 | 21 | 1061 | 28.3 | ||||
| ISO180-21.6-150 | 21.6 | 1087 | 29 | ||||
| ISO180-22.3-150 | 22.3 | 1100 | 29.4 | ||||
| ISO219-20-150 | 219 | 20 | 705 | 27.8 | 150 | 6.1 | 37Mn |
| ISO219-25-150 | 25 | 855 | 32.8 | ||||
| ISO219-27-150 | 27 | 915 | 34.8 | ||||
| ISO219-36-150 | 36 | 1185 | 43.9 | ||||
| ISO219-38-150 | 38 | 1245 | 45.9 | ||||
| ISO219-40-150 | 40 | 1305 | 47.8 | ||||
| ISO219-45-150 | 45 | 1455 | 52.9 | ||||
| ISO219-46.7-150 | 46.7 | 1505 | 54.6 | ||||
| ISO219-50-150 | 50 | 1605 | 57.9 |
Being a professional manufacturer of gas cylinders, we can produce high-quality seamless steel gas oxygen cylinders from 2L to 68L with different stadard specifications as per your kind request(s). If any interests or some more info needed, pls feel free to contact us!
| Material: | Steel |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Oxygen |
| Structure: | General Cylinder |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Pressure Direction: | Single-acting Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
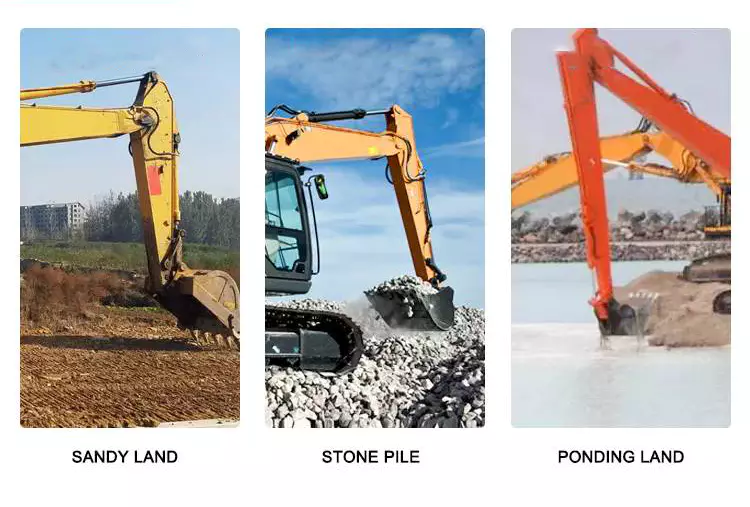

What advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have improved sealing and reliability?
Advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have continuously contributed to improving sealing and reliability in hydraulic systems. These advancements aim to address common challenges such as leakage, wear, and failure of seals, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are several key advancements that have significantly improved sealing and reliability in hydraulic cylinders:
1. High-Performance Sealing Materials:
- The development of advanced sealing materials has greatly improved the sealing capabilities of hydraulic cylinders. Traditional sealing materials like rubber have been replaced or enhanced with high-performance materials such as polyurethane, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), and various composite materials. These materials offer superior resistance to wear, temperature, and chemical degradation, resulting in improved sealing performance and extended seal life.
2. Enhanced Seal Designs:
- Advancements in seal designs have focused on improving sealing efficiency and reliability. Innovative seal profiles, such as lip seals, wipers, and scrapers, have been developed to optimize fluid retention and prevent contamination. These designs provide better sealing performance, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage and maintaining system integrity. Additionally, improved seal geometries and manufacturing techniques ensure tighter tolerances, reducing the potential for seal failure due to misalignment or extrusion.
3. Integrated Seal and Bearing Systems:
- Hydraulic cylinders now incorporate integrated seal and bearing systems, where the sealing elements also serve as bearing surfaces. This design approach reduces the number of components and potential failure points, improving overall reliability. By integrating seals and bearings, the risk of seal damage or displacement due to excessive loads or misalignment is minimized, resulting in enhanced sealing performance and increased reliability.
4. Advanced Coatings and Surface Treatments:
- The application of advanced coatings and surface treatments to hydraulic cylinder components has significantly improved sealing and reliability. Coatings such as chrome plating or ceramic coatings enhance surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. These surface treatments provide a smoother and more durable surface for seals to operate against, reducing friction and improving sealing performance. Moreover, specialized coatings can also provide self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for additional lubrication and enhancing reliability.
5. Sealing System Monitoring and Diagnostic Technologies:
- The integration of monitoring and diagnostic technologies in hydraulic systems has revolutionized seal performance and reliability. Sensors and monitoring systems can detect and alert operators to potential seal failures or leaks before they escalate. Real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and seal performance parameters allows for proactive maintenance and early intervention, preventing costly downtime and ensuring optimal sealing and reliability.
6. Computational Modeling and Simulation:
- Computational modeling and simulation techniques have played a significant role in advancing hydraulic cylinder sealing and reliability. These tools enable engineers to analyze and optimize seal designs, fluid flow dynamics, and contact stresses. By simulating various operating conditions, potential issues such as seal extrusion, wear, or leakage can be identified and mitigated early in the design phase, resulting in improved sealing performance and enhanced reliability.
7. Systematic Maintenance Practices:
- Advances in hydraulic cylinder technology have also emphasized the importance of systematic maintenance practices to ensure sealing and overall system reliability. Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of seals, as well as routine system flushing and filtration, help prevent premature seal failure and optimize sealing performance. Implementing preventive maintenance schedules and adhering to recommended service intervals contribute to extended seal life and enhanced reliability.
In summary, advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have led to significant improvements in sealing and reliability. High-performance sealing materials, enhanced seal designs, integrated seal and bearing systems, advanced coatings and surface treatments, sealing system monitoring and diagnostics, computational modeling and simulation, and systematic maintenance practices have all played key roles in achieving optimal sealing performance and increased reliability. These advancements have resulted in more efficient and dependable hydraulic systems, minimizing leakage, wear, and failure of seals, and ultimately improving the overall performance and longevity of hydraulic cylinders in diverse applications.
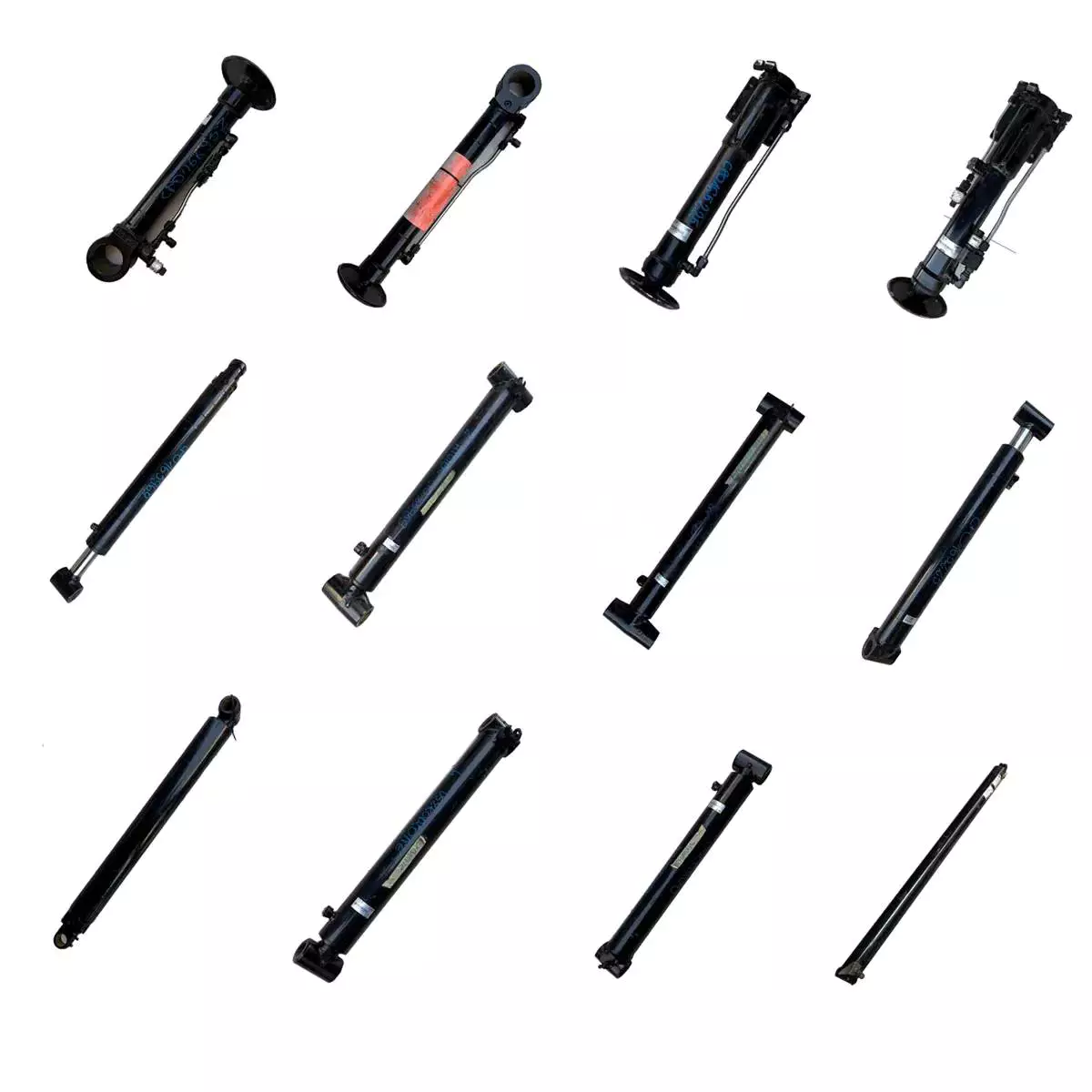

Ensuring Controlled and Safe Force Application in Heavy Machinery with Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders play a critical role in heavy machinery by ensuring controlled and safe force application. The ability to exert and control high forces is essential for heavy machinery operations, such as lifting, pressing, pushing, or pulling heavy loads. Let's explore how hydraulic cylinders ensure controlled and safe force application in heavy machinery:
- Force Control: Hydraulic cylinders provide precise force control capabilities. The hydraulic system's pressure can be adjusted to regulate the force exerted by the cylinder. This control allows operators to apply the necessary force for a specific task while ensuring it remains within safe limits. By accurately controlling the force, hydraulic cylinders help prevent excessive force that could damage the machinery or compromise the safety of the operation.
- Load Balancing: In heavy machinery, multiple hydraulic cylinders are often used in conjunction to distribute and balance the applied force. By using multiple cylinders, the load can be evenly distributed across the machinery, minimizing stress concentrations and ensuring controlled force application. This load balancing approach enhances the stability and safety of the machinery, preventing uneven loading that could lead to structural issues or instability.
- Safety Valves: Hydraulic systems in heavy machinery are equipped with safety valves to protect against excessive force or overloading. Safety valves are designed to release hydraulic fluid from the cylinder when the force exceeds a predetermined threshold. This prevents the force from reaching dangerous levels, safeguarding the machinery and preventing potential accidents or damage. Safety valves provide an additional layer of safety and ensure controlled force application even in unexpected circumstances.
- Pressure Relief Systems: Hydraulic cylinders incorporate pressure relief systems to further enhance safety. These systems are designed to relieve excess pressure in the hydraulic system, which could occur due to factors such as thermal expansion or system malfunctions. By relieving excess pressure, the pressure relief systems prevent sudden and uncontrolled force surges, maintaining safe and controlled force application in heavy machinery.
- Structural Integrity: Hydraulic cylinders are designed to withstand the high forces and loads associated with heavy machinery applications. The cylinders are constructed using robust materials, such as high-strength steel, and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their structural integrity. This ensures that the cylinders can safely handle the forces applied during heavy machinery operations without experiencing failures or deformations that could compromise the safety and controlled force application.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders ensure controlled and safe force application in heavy machinery through force control, load balancing, safety valves, pressure relief systems, and robust structural design. These features and design considerations enable operators to exert the necessary force while maintaining safety and preventing excessive loads or force surges. By incorporating hydraulic cylinders into heavy machinery, manufacturers can achieve controlled force application, enhance operational safety, and protect the machinery from damage or failure.
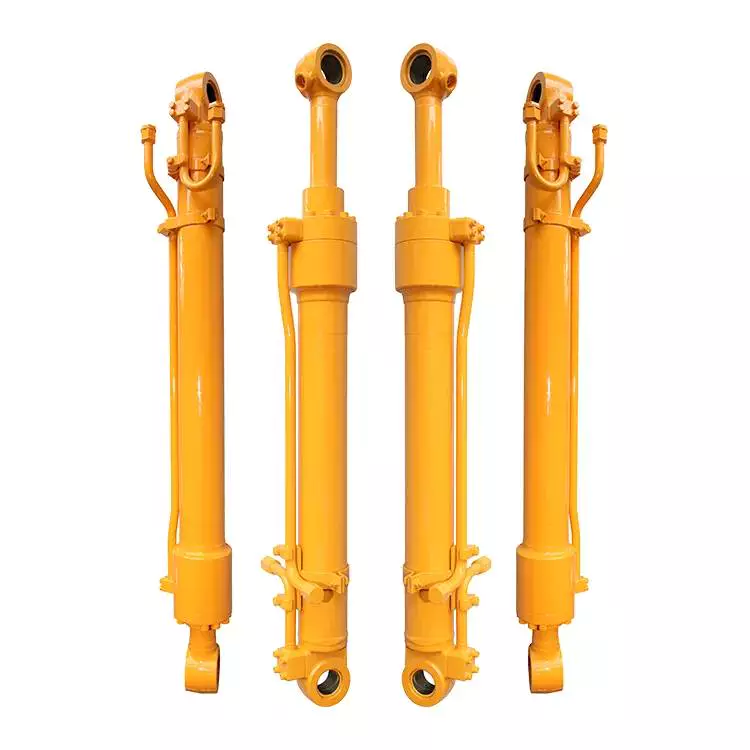

What maintenance practices are essential for extending the lifespan of hydraulic cylinders?
Maintaining hydraulic cylinders is crucial for extending their lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance helps prevent premature wear, damage, and failure, ultimately reducing downtime and saving costs. Here are some essential maintenance practices to consider for extending the lifespan of hydraulic cylinders:
1. Regular Inspections:
- Conduct routine visual inspections of hydraulic cylinders to identify any signs of damage, leaks, or wear. Inspect the cylinder body, piston rod, seals, and mounting points. Look for fluid leaks, rust, dents, or any abnormal wear patterns. Early detection of issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage and extending the lifespan of the cylinder.
2. Cleanliness:
- Maintain a clean environment around hydraulic cylinders to prevent contaminants from entering the system. Dust, dirt, and debris can damage seals and other internal components, leading to accelerated wear and reduced performance. Regularly clean the cylinder and its surroundings to minimize the risk of contamination.
3. Proper Lubrication:
- Adequate lubrication is critical for the smooth operation and longevity of hydraulic cylinders. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricant. Apply lubrication to the cylinder's moving parts, such as the piston rod, to reduce friction and minimize wear.
4. Seal Maintenance:
- Seals play a vital role in preventing hydraulic fluid leaks and maintaining the cylinder's performance. Inspect and replace worn or damaged seals promptly. Ensure that seals are properly installed and lubricated. Regularly clean the seal grooves to remove any debris that could compromise seal effectiveness.
5. Pressure Checks:
- Periodically check the hydraulic system's pressure to ensure it is within the recommended operating range. Excessive pressure can strain the cylinder and its components, leading to premature wear. Monitor pressure levels and make adjustments as necessary to prevent overloading the cylinder.
6. Control Valve Maintenance:
- Maintain and inspect control valves that regulate the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid. Ensure that the valves are functioning correctly and not causing excessive stress or pressure spikes in the cylinder. Clean or replace control valves if they are damaged or malfunctioning.
7. Cylinder Alignment:
- Proper alignment of hydraulic cylinders is essential for their longevity. Misalignment can cause excessive side loads, leading to uneven wear and potential damage. Ensure that the cylinder is correctly aligned with other components and that the mounting points are secure.
8. Preventing Overloading:
- Avoid subjecting hydraulic cylinders to loads exceeding their rated capacity. Overloading can cause internal damage, seal failure, and reduced lifespan. Ensure that the load requirements are within the cylinder's capabilities and consider using safety devices like overload protection systems when necessary.
9. Training and Operator Awareness:
- Provide proper training to equipment operators on the correct use and handling of hydraulic cylinders. Operators should be aware of the cylinder's limitations, safe operating procedures, and the importance of regular maintenance. Promote a culture of proactive maintenance and encourage operators to report any potential issues promptly.
10. Documentation and Record-Keeping:
- Maintain detailed documentation of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and replacements. Keep records of lubrication schedules, pressure checks, and any maintenance performed on the hydraulic cylinders. This documentation helps track the cylinder's history, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance effectively.
By following these maintenance practices, hydraulic cylinder lifespan can be extended, ensuring reliable performance and reducing the risk of unexpected failures. Regular inspections, cleanliness, proper lubrication, seal maintenance, pressure checks, control valve maintenance, cylinder alignment, preventing overloading, operator training, and documentation contribute to the overall longevity and optimal functioning of hydraulic cylinders.

editor by CX 2023-12-01